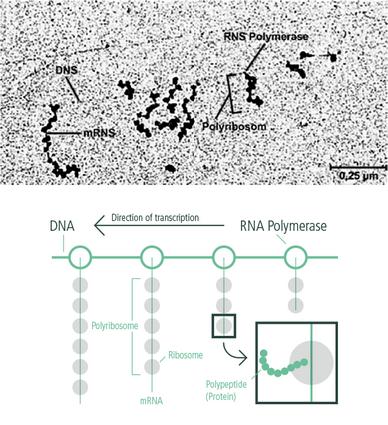
Whenever the cell requires a certain protein, the gene for this protein is transcribed into a messenger molecule, the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid). This copying process - called transcription - requires a specific enzyme, the RNA polymerase. The mature mRNA is then translated into the protein by a ribosome. This process is termed translation. This flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein takes place in all living organisms and is therefore (almost) universal. This sequence of events is therefore also known as the "central dogma of molecular biology".
Split genes
This discovery provided one of the great surprises of 20th century molecular biology: genes of complex organisms are not present as continuous sections on DNA.